Single Crystal Growth Techniques

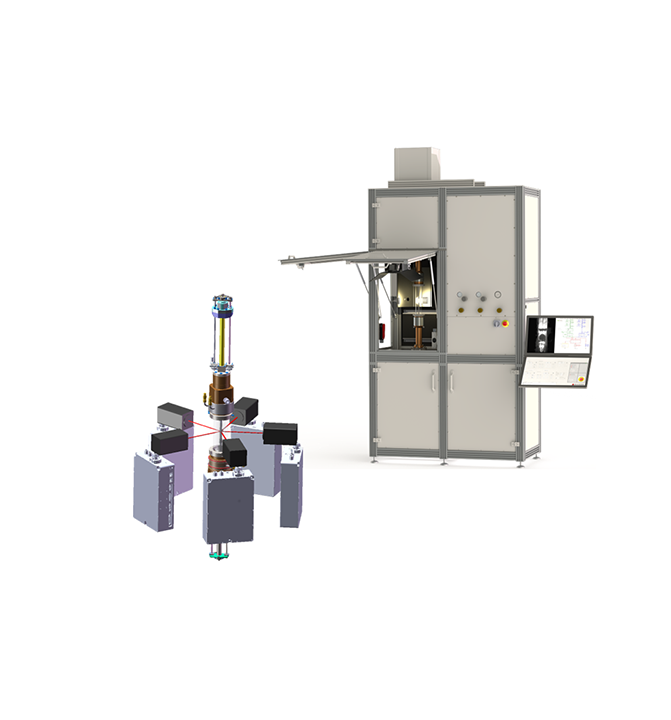
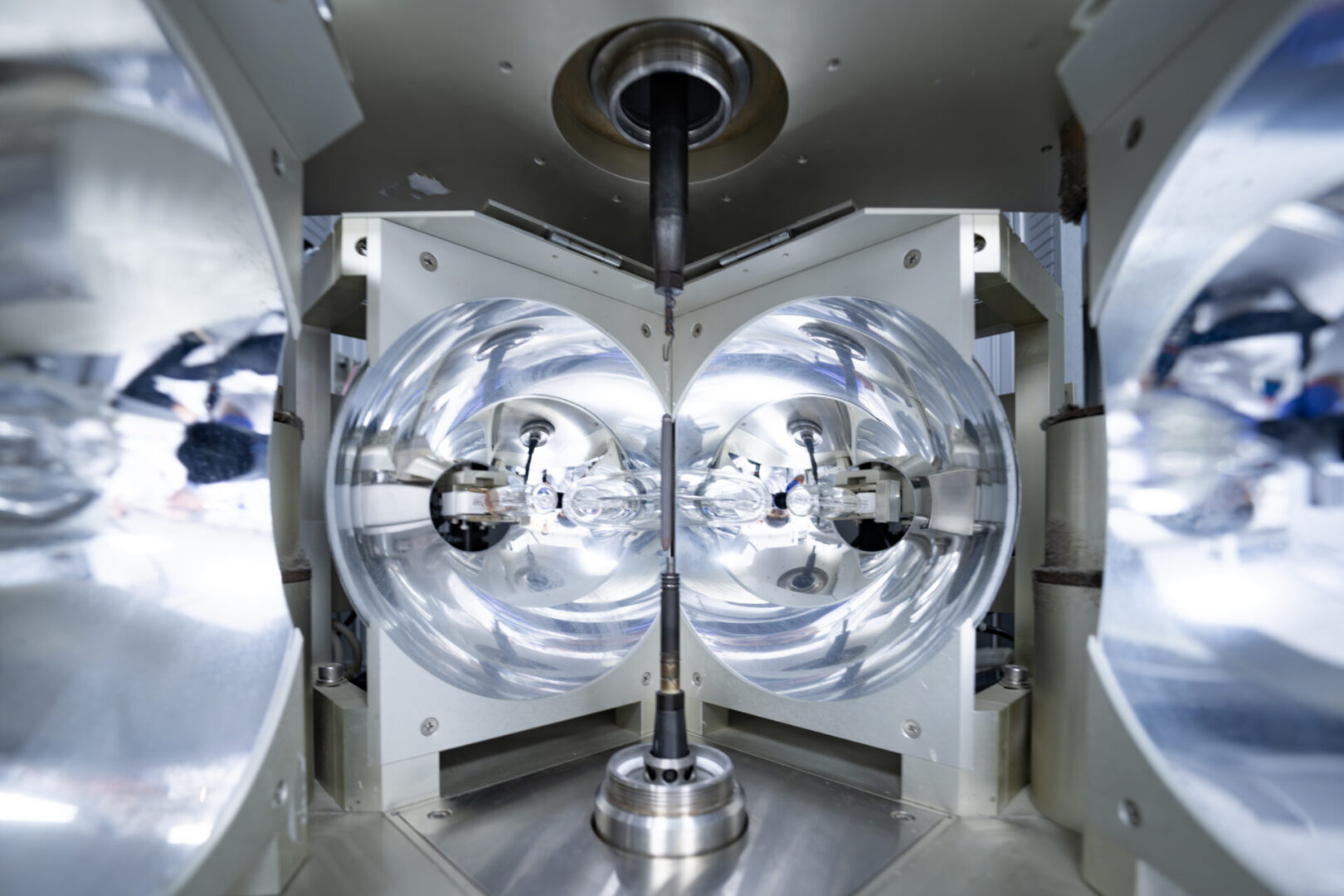
Laser-Heated Floating Zone Growth from SciDre
Laser-Heated Floating Zone (LH-FZ) growth operates at ultra-high pressures, similar to optical floating zone methods. The laser-heated liquid zone allows for higher temperatures and enhanced stability of the molten zone, which supports the growth of a wider range of materials. At pressures up to 300 bar, volatile constituents are suppressed, enabling the synthesis of materials that are otherwise difficult to grow.
Front view of the modular 5 × 300 W diode laser-heated FZ furnace with a rectangular beam profile and advanced process gas management up to 300 bar.
For more information, visit SciDre's website.
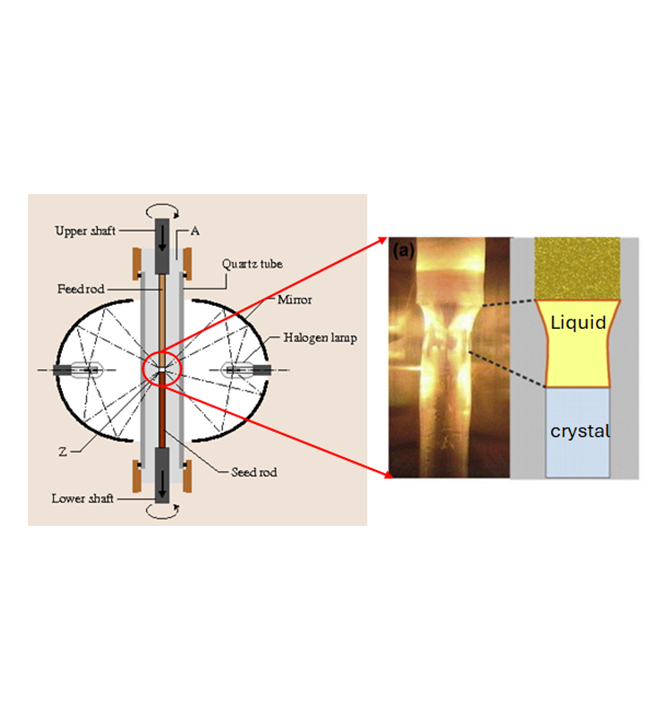
Optical Floating Zone Growth: A Versatile Crystal Growth Solution
Optical Floating Zone (OFZ) growth uses focused optical light from a halogen bulb to locally melt a feed rod, transforming polycrystals into single crystals. This method reaches temperatures up to, 2200 °C using a gas pressure of 10 bar. The crucible-free process results in high-purity crystals with minimal impurities and is suitable for congruently melting oxides, sulphides, and inter-metallics. However, it is unsuitable for volatile compounds and incongruently melting materials. Typical crystal sizes are 1-10 grams.
For more details, visit Crystal System Inc.

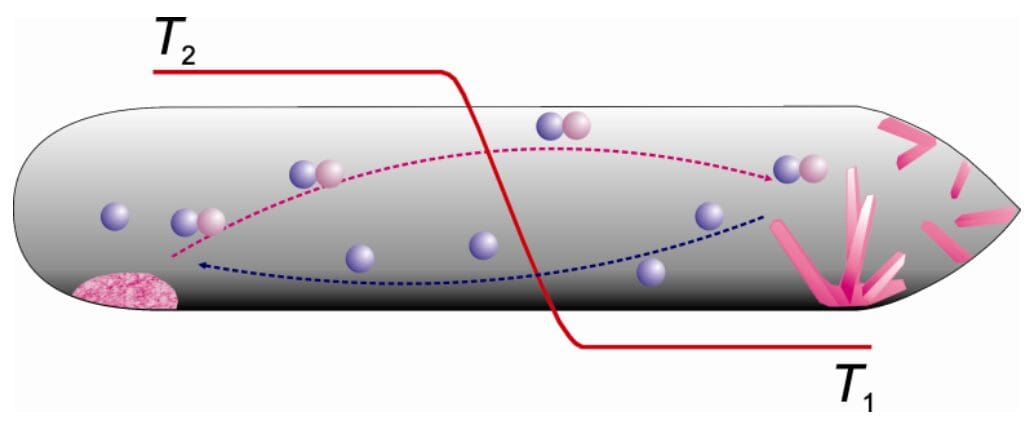
Chemical Vapour Transport Growth (CVT)
Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT) growth involves using a transport agent to drive the growth of a compound via a temperature gradient. This process utilises a gradient temperature zone tube furnace. Samples are sealed inside quartz tubes with transport agents via a gas torch. Typical transporting agents include I₂, Br₂, Cl₂, HCl, NH₄Cl, H₂, H₂O, AlCl₃, and CO. CVT is effective for high-volatility constituents, especially chalcogenides, and typically yields small crystals (~1 mm).
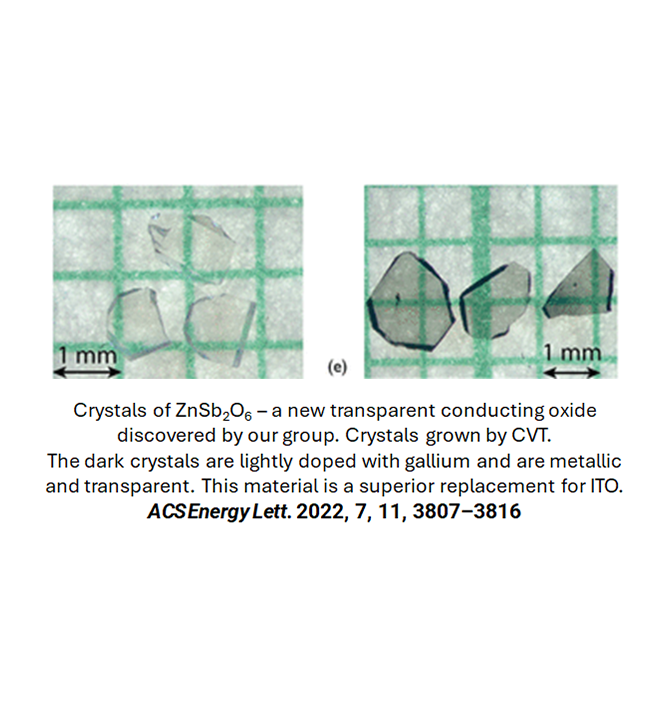
High-Temperature Solvent Growth
High-Temperature Solvent Growth involves crystal precipitation from a molten solvent (or flux) driven by temperature-induced supersaturation. This method is used for growing crystals like strontium iridates from an SrCl₂ solvent, known for their Kitaev magnetism and topological order.

Crystal Alignment, Cutting, and Polishing
Expert services in crystal alignment, cutting, and polishing to ensure the highest quality and precision for your applications.
Connect for More Details
Explore how our advanced crystal growth techniques can meet your needs. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and see how we can assist with your project.



